Describe What Isomers Are and How They Apply to Carbohydrates.
Compare and contrast the two components of starch. Explain isomerism in detail.
Sugars are mainly providing living things with _____.

. Overview and Key Difference 2. The following points highlight the top five classifications of isomerism. The basis for the designation of the isomers of all carbohydrates is glyceraldehyde.
Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. CARBOHYDRATES Before studying carbohydrates we will review and examine isomerism. Sugars are mainly providing living things with _____.
How are dissacharides formed. Describe what isomers are and how they apply to carbohydrates. Structures properties important carbs how they form cyclic molecules and how some of those cyclic molecules can join and dis-join each o.
What is the difference between hexose and pentose sugar stricture. Some of the most common types are trioses three carbons pentoses five carbons and hexoses six carbons. A second type of isomer seen in carbohydrates are diastereoisomers.
Describe what isomers are and how they apply to carbohydrates. By this convention trioses pentoses hexoses are all oligosaccharides. It is the simplest carbohydrate which has optical isomerism.
An Introduction to Carbohydrates. List 3 disaccharides and the monosac charides that form them. Explain briefly how the isomeric structure of a carbohydrate may affect its chemical behavior.
Explain the difference between a ribose and a deoxyribose sugar. Describe what isomers are and how they apply to carbohydrates. Identify acetal and hemiacetal bonding patterns in carbohydrates.
Structural isomers and optical isomers are common in organic compounds such as carbohydrates. Two carbohydrates are said to be enantiomers if they are nonsuperimposable mirror images of one another. Glucose galactose and fructose are monosaccharide isomers.
D and L 2. Top 5 Classifications of Isomerism Carbohydrates. List 3 disaccharides and the monosaccharides that form them.
Describe the three main polysaccharides and their functions. There are two types of isomerism. How are dissacharides formed.
Monosaccharides are simple sugars made up of three to seven carbons and they can exist as a linear chain or as ring-shaped molecules. Glucose fructose and galactose are some of the examples of monosaccharide isomers They all tend to have the same chemical formula but they are varied in terms of structure and chemical nature. Mention the isomers of glucose and explain what kind of isomers they are.
D Simple sugars are molecules with the simple formula CnH2nOn. Define a functional group and Describe the functional. Image modified from OpenStax Biology.
Isomers are ions or mol - ecules that have identical formulas but have different structures. Describe the three main polysaccharides and their functions. An example of an enantiomer is the D and L isomers of glucose as shown by the figure to the right.
Glucose glucose forms maltose glucose fructose forms sucrose. What are Structural Isomers in Carbohydrates 3. Pyranose and Furanose Ring Structures 5.
α- and β-anomers 3. Formed when they are connected by a glycosidic bond. Sugars are also named according to their number of carbons.
C Carbohydrates are hydrates of amino acids. The two propanol isomers consist of propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol also known as isopropyl alcohol which are distinguished by the placement of an oxygen atom either on the terminal carbon atom or the central carbon atom respectively. Trioses have 3-C atoms tetroses have 4-C atoms pentoses have 5-C atoms and hexoses have 6-C atoms.
Click on Nucleic Acids. Compare and contrast amylopectin and glycogen. Carbohydrates formed by the condensation of 2-9 monomers are called oligosaccharides.
Isomers apply to carbohydrates that are described as follows. Complex Carbohydrates Polysaccharides Complex carbohydrates have two or more sugar molecules hence they are referred to as starchy foods. Glucose galactose and fructose are monosaccharide isomers which means they all have the same chemical formula.
How are dissacharides formed. Carbohydates Monosaccharides Isomers Stereoisomers Numbering of Carbon Atoms Asymmetric Carbon Atoms Trioses and Pentoses Hexoses Isomers The monosaccharides can be divided into groups based on the number of carbon atoms in the molecules thus. Describe what isomers are and how they apply to carbohydrates.
Fructose galactose and glucose are isomers with the chemical formula There are. B Carbohydrates include only polyhydroxy aldehydes. A four-carbon monosaccharide with an aldehyde carbonyl group at carbon-1.
Carbohydrates are often isomers - meaning they have the same atomic composition but different structures. Describe the three main polysaccharides and their functions. List 3 disaccharides and the monosaccharides that form them.
Glucose and fructose are structural isomers. Describe the structural and. Structural Isomers and Stereoisomers In unit 7 we defined isomers as compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
Glucose and its isomers One important monosaccharide is glucose a six-carbon sugar with the formula. Isomers will have different bonding properties and will form different disaccharides and macromolecules depending on the isomer involved eg. Isomers are classified into two major categories namely structural and stereoisomers.
Understand the difference between homopolysaccharides and heteropolysaccharides.

Erythrose And Threose Chemistry Organic Chemistry Opposites

Carbohydrates Definition Structure Types Examples Functions

D Glucose And L Glucose Are Enantiomers While D Glucose And D Mannose Are Epimers Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry D Glucose

D And L Glucose Are Enantiomers Chemistry Science Chemistry Organic Chemistry
Carbohydrates Chemistry Master

Pin By Michelle Sneag Thorne On Life Sciences Answer Keys Answers Worksheets

Carbohydrates For The Mcat Everything You Need To Know Shemmassian Academic Consulting

Carbohydrate Configuration Britannica

Describe What Isomer Are And How They Apply To Carbohydrates Brainly Com

Carbohydrate Stabilization Using Formaldehyde Fa A Preventing Download Scientific Diagram

How To Get A Job Flow Chart Flow Chart Template App Development Process

Carbohydrate Summary Britannica
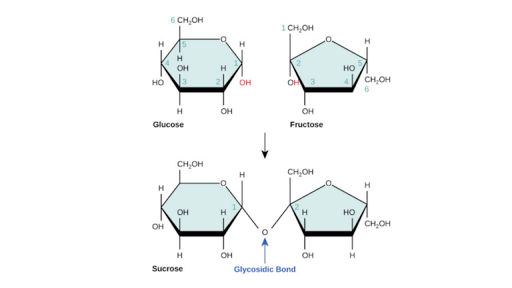
Carbohydrates Article Chemistry Of Life Khan Academy
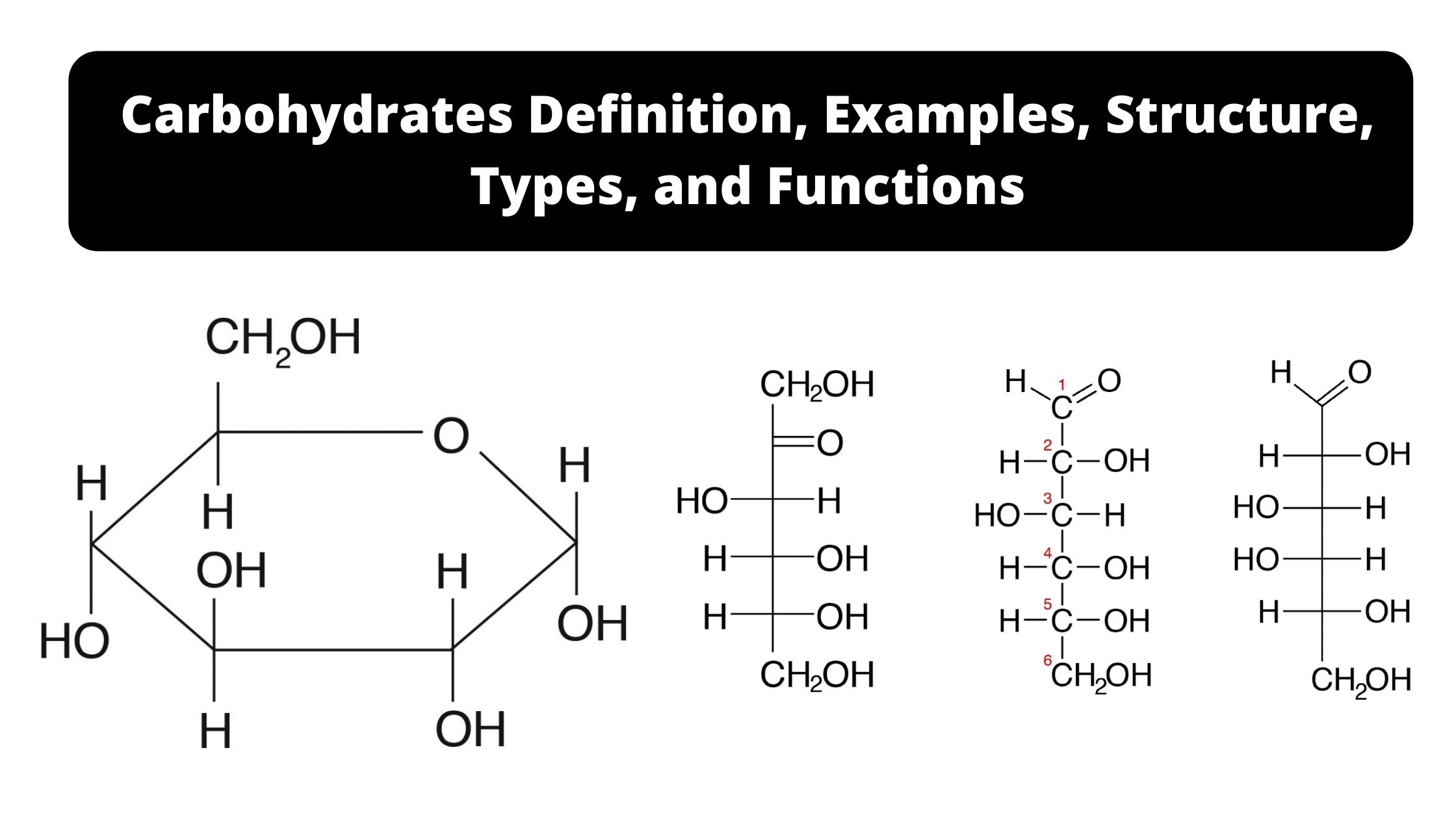
Carbohydrates Definition Examples Structure Types And Functions






Comments
Post a Comment